Behind the Scenes: How Interchange Fees works?
Every time a transaction is made via a card scheme (Visa, Mastercard, etc.), the acquirer pays the cardholder’s bank an interchange fee. The business then pays the interchange fee back as part of its card processing fees.
What is Interchange++?
Interchange++ is a pricing model used in the payment processing industry, particularly for credit card transactions. This pricing structure provides transparency compared to other methods, offering a more comprehensive breakdown of your expenses. This pricing structure is often preferred by businesses that want a clear view of what they're paying for in terms of interchange fees and processing charges.
What is Interchange++ structure?
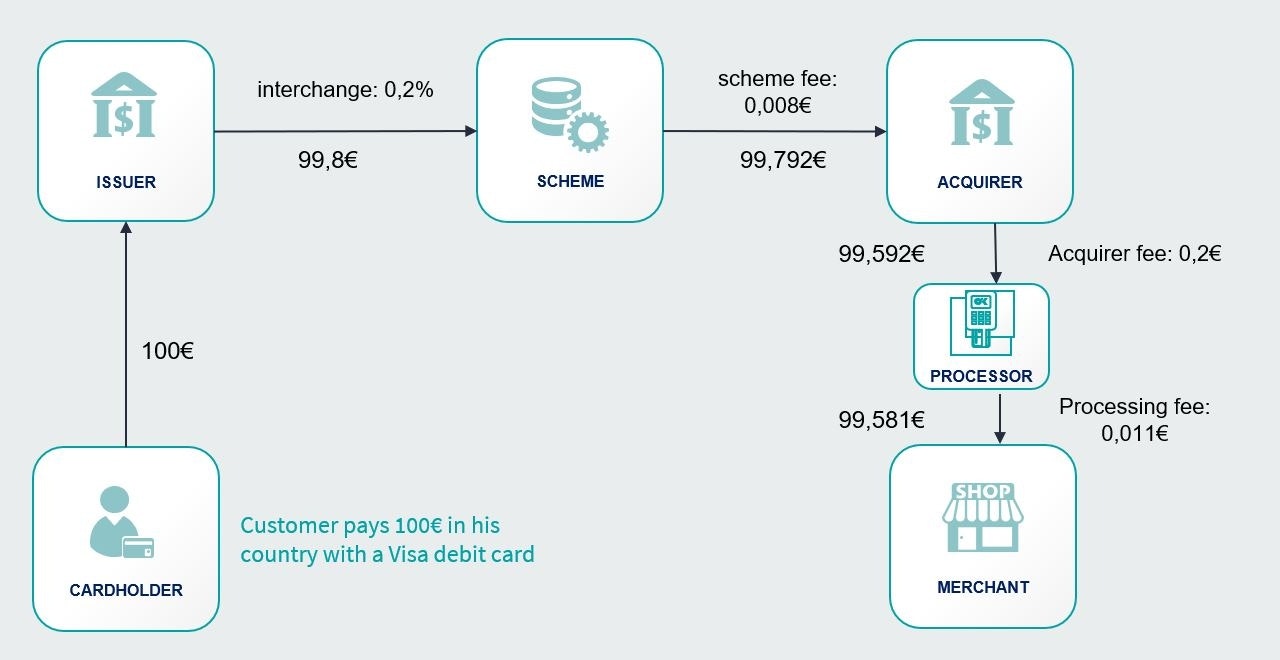
When a card transaction is processed, there are three different cost components:
The interchange fee that goes to the card issuing bank.
The scheme fee that goes to Visa or Mastercard (first +)
The acquirer fee (second +)
What is interchange used for?
Interchange fees serve several useful purposes in the payment processing ecosystem:
Incentivizing Issuers: They incentivize banks and financial institutions to issue credit cards and offer various cardholder benefits and rewards programs.
Payment Network Maintenance: They fund the infrastructure and maintenance of payment networks like Visa and Mastercard, ensuring their continued operation and security.
Global Payment Ecosystem: They facilitate international transactions by providing a common framework for cross-border payments.
Funding Innovation: Interchange fees enable continuous innovation in payment technology and the development of new payment solutions.
How is interchange defined?
Interchange fee is set by card schemes (Visa, Masterd...) and varies according to the type of transaction, the product involved and from country to country.
Since 9 December 2015, an EU regulation (Regulation (EU) 2015/751) on interchange fees imposes interchange fee caps on most product types within the European Economic Area (EEA).
This regulation on interchange fees introduced caps to limit fees but also:
Promote transparency,
Encourage competition in the payment industry,
In overall, it benefits consumers and merchants while fostering innovation.
You can consult scheme's website to access to interchange fees directly: